EDS2100 and EDS4100 RS485 RX Biasing
On the EDS2100 and EDS4100 how do I use RX Biasing to ensure that the data lines on an RS485 connection are at a known state when the line is idle?
When an RS-485 network is in an idle state, all nodes are in a high impedance listen or receive mode. Under this condition there are no active drivers on the RS-485 network. This condition is commonly referred to as tristate. When in this mode the RS485 device effectively "disappears" from the network.
Without anything driving the network, the electrical state of the data lines is unknown. In order to maintain a minimum 200 mV differential between the "A" line and the "B" line, bias resistors must be applied to force the data lines into a known idle condition.
This can be accomplished by adding 1K ohm biasing resistors between the Data+ pin(s) and +5V and between the Data- pin(s) and GND on the RS485 ports of the EDS4100, port 1 and 3..
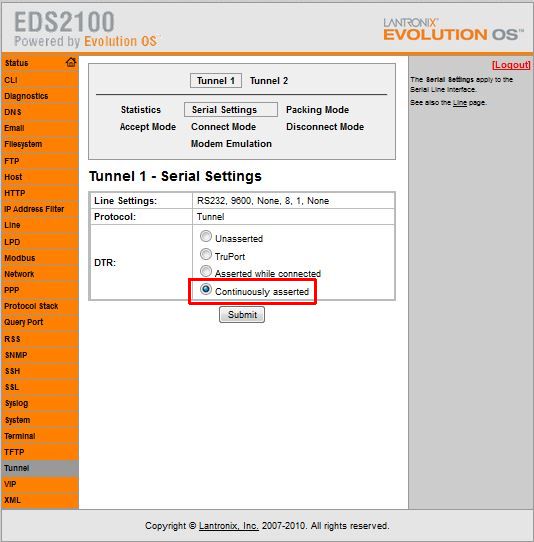
Since there is no 5V signal on the EDS2100/EDS4100's connector the DTR output signal can be used as a source for the 5V signal. Configure DTR to be "Continously Asserted" as shown below:
On a 4-wire connection connect four 1K resistors as shown. Pin numbers are in parentheses:
RX+ (2) to DTR (4)
TX+ (7) to DTR (4)
RX- (8) to GND (5)
TX- (3) to GND (5)
On a two-wire connection connect 2 resistors:
Data+ (7) to DTR (4)
Data- (3) to GND (5)
[Originally Published On: 06/24/2009 12:51 PM]